Mechanism Used to Describe the Spreading of Oceanic Crust Is
Seafloor spreading is the mechanism for Wegeners drifting continents. In the plate tectonics theory the lithosphere is divided into ____.

Plate Tectonics Toward A Unifying Theory Britannica
Oceanic crust contains a higher percentage of oceanic ridges than ocean basin floors.

. It may be surprising considering that parts of the continental crust are close to 4000 Ma old that the. What evidence in the oceanic crust finally confirmed the hypothesis of seafloor spreading. What was the driving mechanism proposed by Hess to explain sea floor spreading.
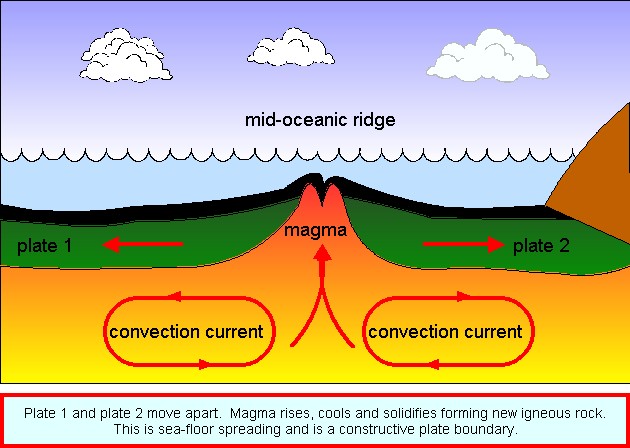
Convection currents within the mantle take the continents on a conveyor-belt ride of oceanic crust that over millions of years takes them around the planets surface. Oceanic crust is about 6 km 4 miles thick. A younger oceanic crust is then formed causing the spread of the ocean floor.
Contents 1 History of study 2 Significance 3 Spreading center 4 Incipient spreading 5 Continued spreading and subduction 6 Debate and search for mechanism. The new rock is dense but not as dense as the old rock that moves away from the ridge. As we discussed in Chapter 10 oceanic crust is formed at sea-floor spreading ridges from magma generated by decompression melting of hot upward-moving mantle rock Figure 1018.
The oldest oceanic crust is around 280 Ma in the eastern Mediterranean and the oldest parts of the open ocean are around 180 Ma on either side of the north Atlantic. The force from volcanic eruptions pushes plates apart. Seafloor spreading is one of the mechanisms that result in continental drift.
Oceanic crust is pulled into the Earths mantle at hotspots Changes in the Earths magnetic field push the plates apart Plates are pulled by oceanic crust that is metamorphosed into very dense rock during subduction The force from volcanic eruptions pushes. A device that bounces sound waves off underwater objects and then records the echoes of these sound waves sea-floor spreading when the sea floor moves apart along both sides of a mid-ocean ridge as new crust is added carrying the continents along with them deep ocean trench deep underwater canyons where the oceanic crust bends downward subduction. Oceanic crust is pulled into the Earths mantle at hotspots.
Irrespective of the exact mechanism the geologic record indicates that the resistance to. During the late 20th and early 21st centuries evidence emerged supporting the notion that subduction zones preferentially initiate along preexisting fractures such as transform faults in the oceanic crust. The breakup of Pangaea by seafloor spreading is seen in this animation.
The mechanisms responsible for initiating subduction zones are controversial. Downwelling oceanic currents b. 5 centimeters per year.
The ages of different parts of the crust are shown in Figure 1822. When the molten magma reaches the oceanic crust it cools and pushes away the existing rocks from the ridge equally in both directions. It is composed of several layers not including the overlying sediment.
Convection currents within the mantle take the continents on a conveyor-belt ride of oceanic crust that over millions of years takes them around the planets surface. Along the ridge molten material that forms several kilometers beneath the surface rises and erupts. If new oceanic crust and lithosphere is continually being created at the oceanic ridges the oceans should be expanding indefinitely unless there were a mechanism to destroy the oceanic lithosphere.
The crust and uppermost mantle. This hypothesis traces oceanic crust from its origin at a mid-ocean ridge to its destruction at a deep sea trench and is the mechanism for continental driftDuring World. World War II gave scientists the tools to find the mechanism for continental drift that had eluded Wegener.
This magma oozes out onto the sea floor to form. Internal convection cells in the Earths mantle. What evidence in the oceanic crust finally confirmed the hypothesis of seafloor spreading.
About 10 of the mantle rock melts under these conditions producing mafic magma. Seafloor spreading theory that oceanic crust forms along submarine mountain zones known collectively as the mid-ocean ridge system and spreads out laterally away from them. Thermal convection cells AND motions in the outer core.
Maps and other data gathered during the war allowed scientists to develop the seafloor spreading hypothesis. Oceanic lithosphere returns to the mantle by sliding downward at the oceanic trenches. 182 The Geology of the Oceanic Crust.
What they discovered was that the. This idea played a pivotal role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics which revolutionized geologic thought during the last quarter of the 20th century. Sea-Floor Spreading begins at a mid-ocean ridge which forms along a crack in the oceanic crust.
10 million years. At the same time older rock moves outward on both sides of the ridge. Differentiate between epicenter and hypocenter.
7 major plates and many smaller plates. Seafloor spreading or Seafloor spread is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge. Changes in the Earths magnetic field push the plates apart.
Thermal convection cells d. A tectonic plate consists of ____. Hot mantle rock rises and spreads at mid ocean ridges.
Basalt the once-molten rock that makes up most new oceanic crust is a fairly magnetic substance and scientists began using magnetometers to measure the magnetism of the ocean floor in the 1950s. It is estimated to take _____ for the oceans volume to circulate through the oceanic crust at spreading centers. Seafloor spreading is the mechanism for Wegeners drifting continents.
Oceanic crust the outermost layer of Earths lithosphere that is found under the oceans and formed at spreading centres on oceanic ridges which occur at divergent plate boundaries. Benioff zones and the oceanic trenches provided the answer. Two continents moving in opposite direction pulls the oceanic crust apart.
The magnetism of mid-ocean ridges helped scientists first identify the process of seafloor spreading in the early 20th century. Plates are pulled by oceanic crust that is metamorphosed into very dense rock during subduction. Motions in the outer core e.
The mechanism used to describe the spreading of oceanic crust is. Hot magma rises to the crusts surface cracks develop in the ocean floor and the magma pushes up and out to form mid-ocean ridges. In places where convection currents rise up towards the crusts surface tectonic plates move away from each other in a process known as seafloor spreading Fig.
The lithospheric plates move an average of ____.

Plate Tectonics Seafloor Spreading Britannica
A Review Of Ridge Subduction Magmatism And M Eurekalert
No comments for "Mechanism Used to Describe the Spreading of Oceanic Crust Is"
Post a Comment